The following information is available for the sale of Product X for June 2016.
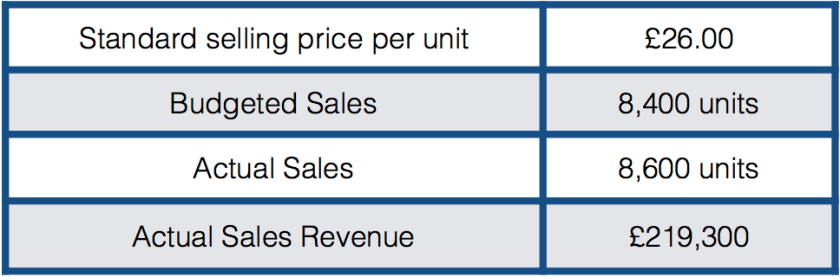
What is the sales price variance for June 2016?
Select ONE answer:
- £4,300 adverse
- £4,300 favourable
- £5,200 adverse
- £5,200 favourable
- £6,500 adverse
Show your workings to arrive at your answer, and explain and justify your reasons:
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
This is multiple choice question is suitable for Accounting KS5 classes.
The answer is 1 – Actual sales revenue divided by actual units sold of 8.600 gives us an average sales price of £25,50, which is 50p less than the standard selling price of £26. The sales price variance, therefore, equals £0.50 * 8,600 or £4,300 which is adverse as the actual sales price achieved of £25.50 is 50p lower than the standard price set in the budget for the month.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.



You must be logged in to post a comment.