Which one of the following is not an example of a cost driver in activity based costing?
Select ONE answer:
- Number of boxes of finished goods shipped
- Number of direct labour hours
- Number of machine set-ups
- Number of production runs
- Number of quality inspections
Explain and define activity-based costing?……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
This is multiple choice question is suitable for Accounting KS5 classes.
The answer is 2 – An activity cost driver is a factor that influences or contributes to the expense of certain business operations. In activity-based costing (ABC), an activity cost driver drives the costs of labor, maintenance or other variable expenses. Cost drivers are essential in ABC, a branch of managerial accounting that allows managers to determine the costs to perform an activity at various activity levels. The most common cost driver has historically been direct labor hours. Expenses incurred relating to the layout or structure of a building or warehouse may utilize a cost driver of square footage to allocate expenses. More technical cost drivers include machine hours, the number of change orders, the number of customer contacts, the number of product returns, the machine setups required for production or the number of inspections.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.



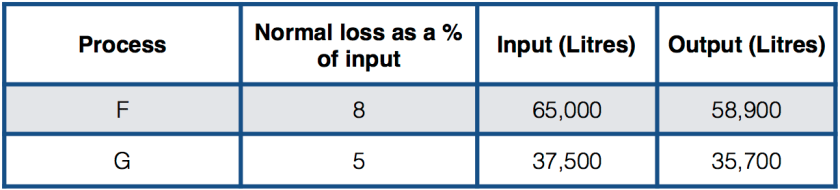
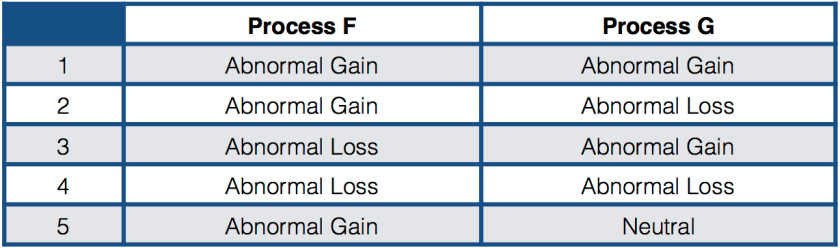
You must be logged in to post a comment.