The production possibility curve for an economy producing capital and consumer goods are shown below.
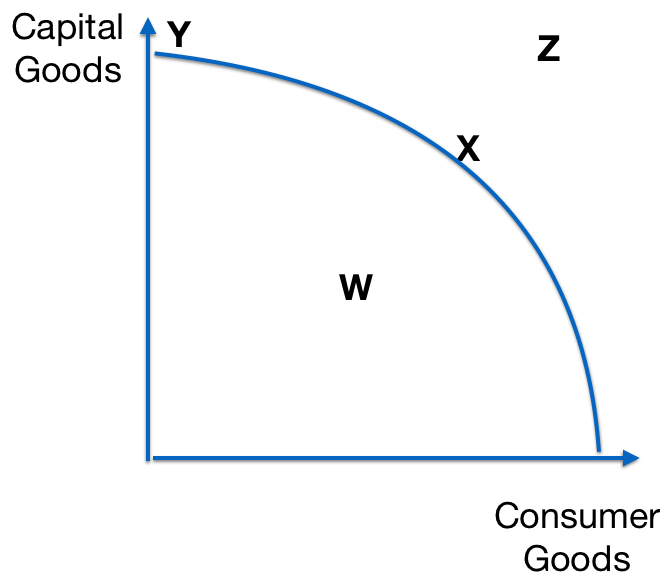
Which production points are currently attainable?
Select ONE answer:
- W only
- X and Y only
- W, X and Y only
- W, X, Y and Z
Show your workings to arrive at your answer, and explain and justify your reasons:……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
This multiple choice question is suitable for Economics KS5 classes.
The answer is 3
- W is attainable as it is inside the curve but it is not the only attainable production point.
- X and Y are attainable as they are on the curve but W is also attainable.
- Correct: W, X and Y are all attainable as they are on or inside the curve – there are sufficient resources to produce these different combinations.
- Z is not currently attainable as it is outside the curve indicating there are not sufficient resources to produce the combination.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.



You must be logged in to post a comment.